Laboratory of Processing and Analysis of Microscopic Images
dr hab. Anna Korzyńska, professor IBBE - head of Lab
prof. dr hab. Włodzimierz Klonowski ✞
mgr inż. Łukasz Roszkowiak,
mgr inż. Jakub Żak
lek. med. Krzysztof Siemion
Methods of analysis of processes observed and monitored on microscopic images and their sequences are investigated in the Laboratory.
The focus of the research are:
- Methods of processing and analysis of microscopic images of stained tissue slices and live cells;
- Support for diagnostic and therapeutic methods and scientific research by development of quantitative analysis of morphology and behaviour of individual cells and their populations;
- Linear and nonlinear analysis of signals and images.
Aiding optical microscopy by quantitative methods of image analysis enables capturing dependence between biological phenomena, e.g.: (1) morphology and behaviour of cells (hepatocytes and fibroblasts with or without genetic modifications [Korzynska et al., 2017]) and (2) conditions of effective proliferation of cells in cell cultures (neuronal stem cells [Korzynska et al., 2005; Korzynska, 2007; Korzynska et al., 2008]).
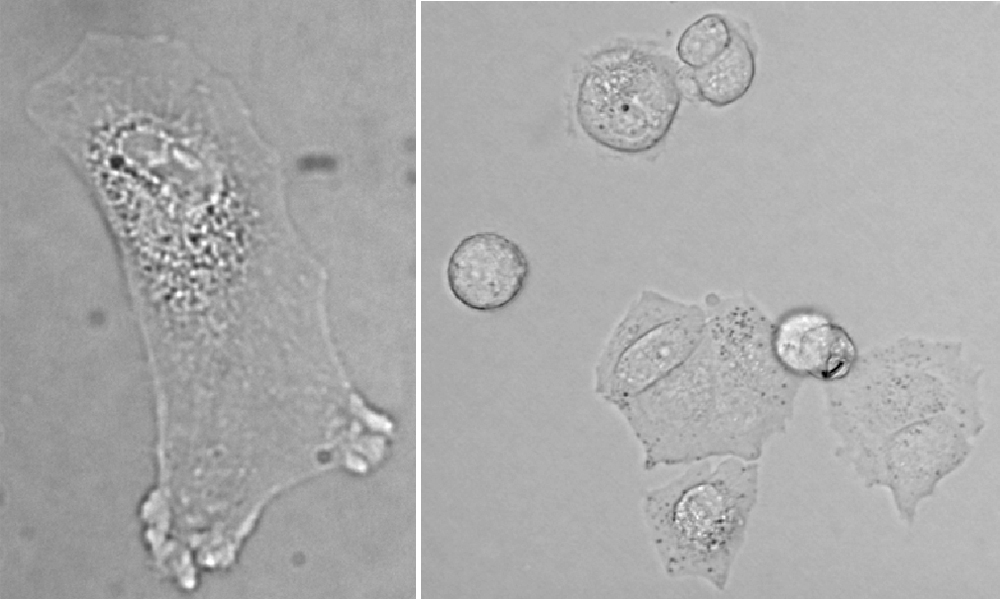
Fig. 1. Images of cells observed in bright field. Left – a fibroblast isolated from human skin. Right – neural stem cells, line HUCB-NSC, in culture.
Although aided by images processing and analysis method quantification of microscopic images of stained thin tissue sections for diagnostic and prognostic has been worked on for quite some time, it still does not produce satisfying results. It seems that digitalization of healthcare would lead to widespread use of virtual slides and automatic assessment. Quantitative analysis methods of nuclei in images of thin tissue sections stained with DAB and hematoxylin have been developed in the Laboratory. The characteristics of tissue images in various diseases (lymphoma, meningioma and breast cancer), with various antibodies used (FoxP3, Ki67) and even of different organs succumbing to the same disease (skin and adenoids in DLBCL) differ widely. Therefore, the methods of processing and analysis images of stained thin tissue sections requited to be tailored to specific cases.
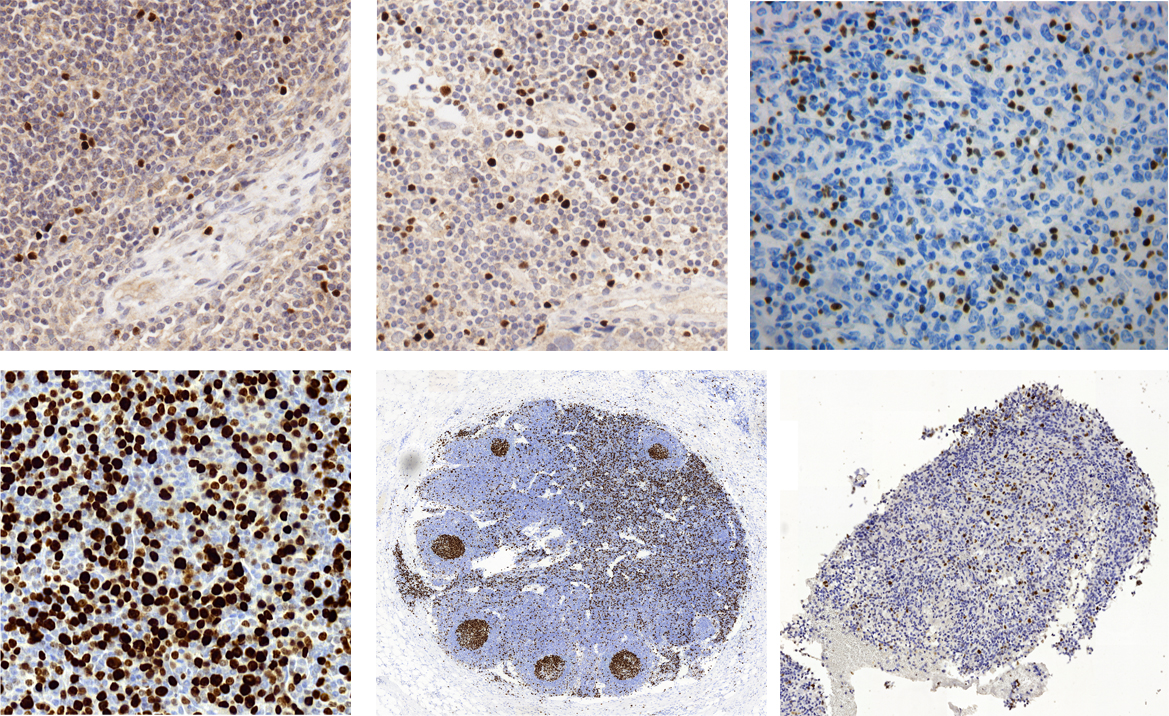
Fig. 2a. Images of fragments stained immunohistochemically with DAB&H:
- Top row – images stained with primary marker against FoxP3 which marking nuclei of T-regulatory cells in tissues (from right): breast cancer, lymphatic node after metastasis, lymphatic node in lymphoma
- Bottom row – images stained with primary marker against Ki67 (proliferation marker) in tissues (from right): skin in DLBCL, healthy lymphatic node, brain in meningioma
In some diseases, the diagnosis or prognosis is based on estimation of number of specific cells, revealed by staining (e.g.: eozyne and hematoxylin or immunohistochemically) and assessment of tissue architecture.
From among published methods of segmentation of images of stained tissues, none are universal. Therefore, they cannot be used to segment any image into immonopositive objects (brown nuclei) and immunonegative objects (blue nuclei), strictly as a pathologist would do. The Laboratory focuses on developing new methods and enhancing those already existing [Korzynska and Zdunczuk, 2008] methods of segmentation, to be used in individual nuclei counting. The knowledge of characteristic properties of microscopic techniques [Korzynska and Iwanowski, 2008; Iwanowski et al., 2009] and the knowledge about cells and tissues [Iwanowski et al., 2010; Callau et al., 2014] is exploded to adjust methods to proposed quantification methods.
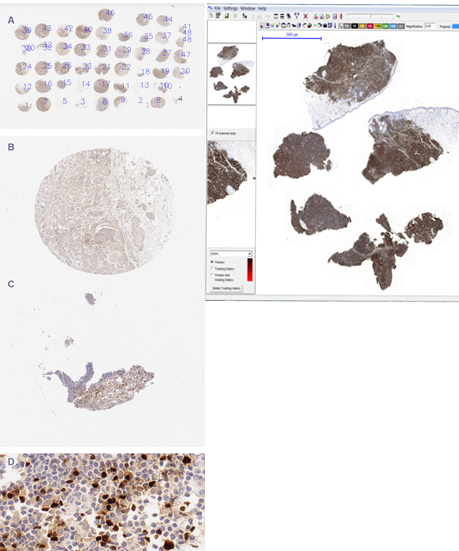
Fig. 2b. TMA and WSI.
The Laboratory has developed algorithms for counting of immunopositive nuclei (brown):
- Method developed in cooperation with Molecular Biology and Research Section and with Pathology Department, both of Hospital de Tortosa Verge de la Cinta. It was financed by the European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST) Action, specifically by Telepathology Network in Europe 2007-2011 (EURO-TELEPATH), symbol IC0604, entitled: “Prospectives on Digital Pathology”, published in 2010 [Korzynska et al., 2010; Korzynska et al, 2013]. The methods is dedicated to analysis of cells marked with FoxP3 in follicular lymphoma.
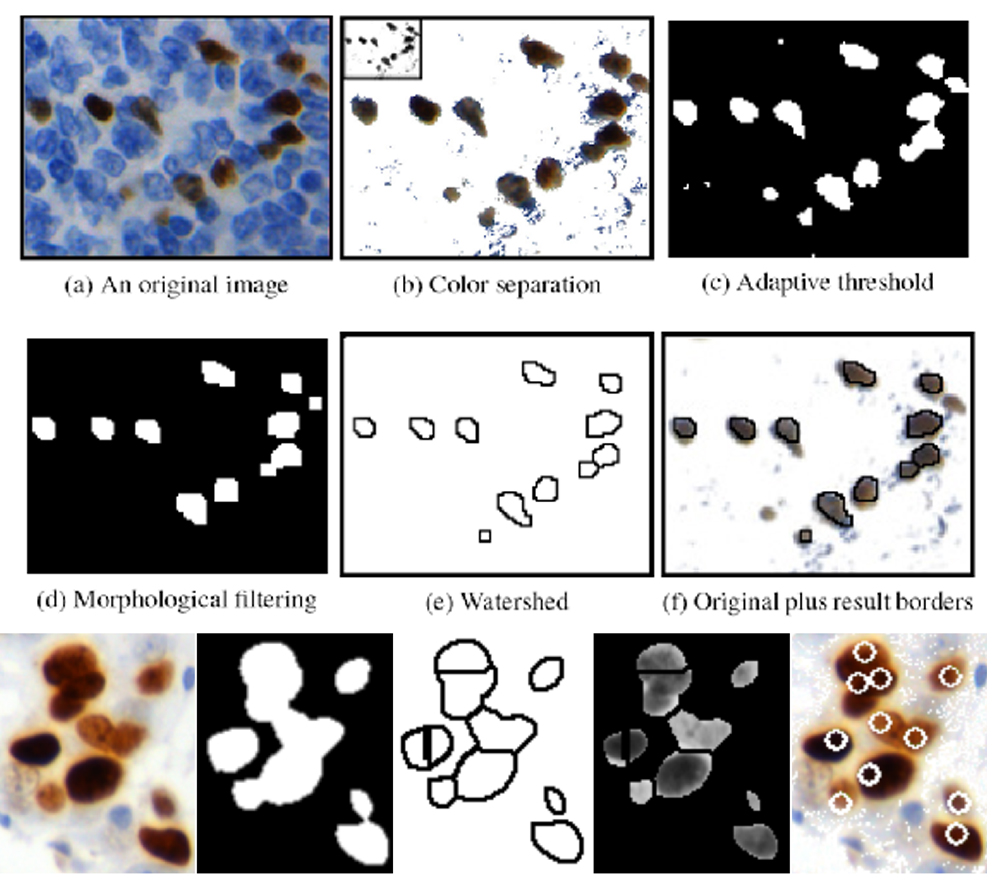
Fig. 3. Method for counting immunoreactive nuclei, based on color separation, adaptive thresholding and watershed.
- METINUS method [Roszkowiak et al., 2015a; Roszkowiak et al, 2015b; Roszkowiak et al., 2016], developed in cooperation with the same centre from Tortosa. Its modification from 2015, METINUS Plus [Korzynska et al., 2017] was developed for projects: “Supporting software to assist pathologist in evaluation of immunohistochemically stained tissue samples of breast cancer stained with DAB&H” and “Automated analysis of tumor microenvironment in triple negative breast cancer without complete pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Predictive factor of relapse”. It concerns analysis of a number of T-regulatory cells in breast cancer images from two groups (1) with or (2) without metastases to lymph nodes.
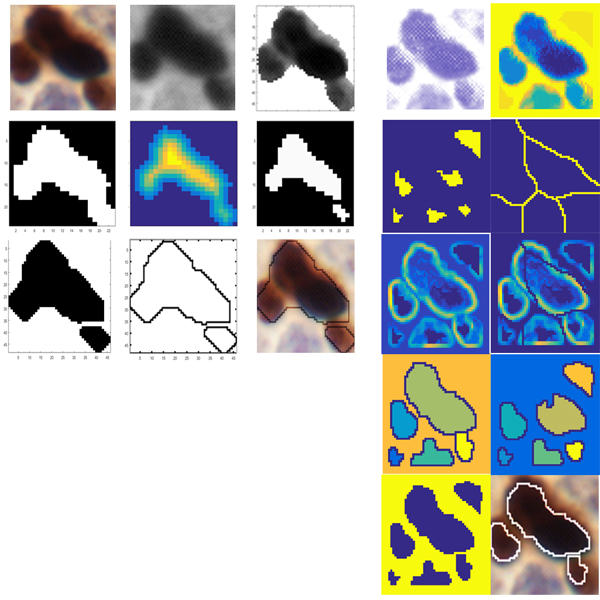
Fig. 4. Metinus and MetinusPlus methods, using brightness dispersion of immunoreactive nuclei and modified watershed (right columns).
- MetPiKi67 method from 2015 [poster] for the project “Web-based platform for the computer analysis of microscopic images to support the pathological diagnosis” and its modification MetPiKi67bis from 2017, developed for IBBE statue (yet unpublished), allow analysis of images of stained tissues from DLBCL.
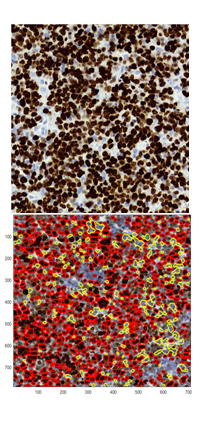
Fig. 5. Results of MetPiKI67.
Proposed methods were used by cooperating physicians to study and develop a model of immunological response in breast cancer [Lopez et al., 2014; Callau et al., 2014] and analysis of microenvironment of triple negative breast cancer, which does not completely respond to chemotherapy [Lejeune et al., 2013].
Furthermore, for analysis of histological structures and cytological samples, problems of standardization [Korzynska et al., 2010] and measurement of image quality have been studied. A method of colour correction based on calibration slide has been proposed [Korzynska et al., 2016; Markiewicz et al., 2016].

Fig. 6. Scheme of colour correction algorithm, based on calibration slides.
Another proposed method is software for division of large-area image showing TMA – images of samples from several patients on a single slide and stained at once. The software allows division and description of single samples, according to provided scheme [Roszkowiak et al., 2016].
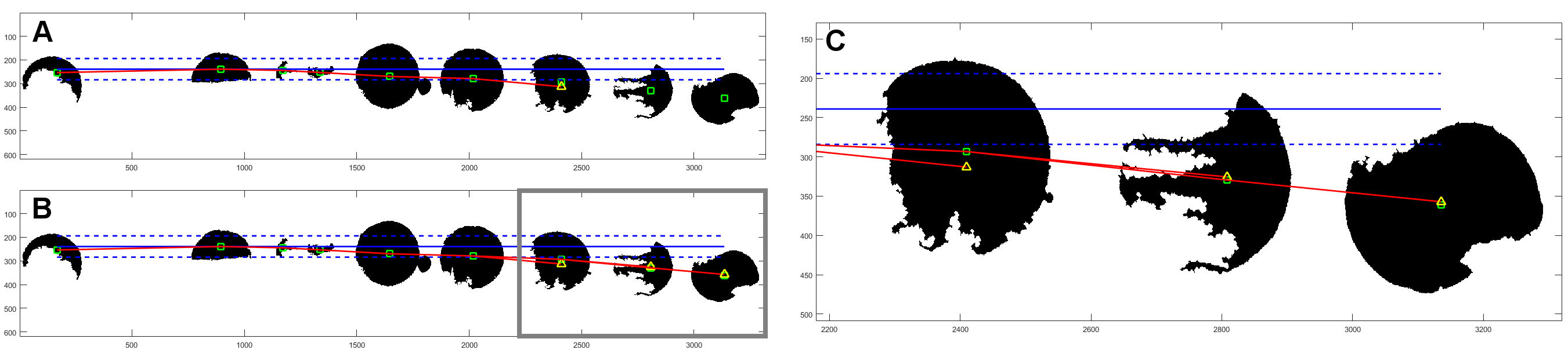
Fig. 7. Scheme of PATMA method.
For the assessment of the quality of quantitative analysis and segmentation methods, tools for creating synthetic microscopic images with desired parameters, have been developed [Iwanowski et al. 2009; Iwanowski et al., 2015a; Korzynska et al.; 2013]. The software for synthetic microscopic images construction was based on SIMPI method [Lehmussola et al., Computational framework for simulating fluorescence microscope images with cell populations. Med Imaging, IEEE Trans. 2007, 26 (7): 1010-1016] and [Lehmussola et al., Synthetic images of high-throughput microscopy for validation of image analysis methods. Proc IEEE. 2008, 96 (8): 1348-1360] and its improvement and extension to adjust it to full color images and to use objects from database.
The Laboratory has concluded following projects:
- “The segmentation method for cells segmentation in sequence of microscopic images” financed by National Sciences Center (NCN), headed by dr Anna Korzyńska, developed from 10.08.2008 to 09.06.2011;
- “Development of automatic quantitative methods for immunohistochemicaly stained tin tissue sections in investigation of immune response in breast cancer” financed by Institute of Health Carlos III in Spain, headed by dr Carlos Lopey from Molecular Biology and Research Section, Hospital Verge de la Cinta w Tortozie, developed from 1.01.2013 to 31.06.2016,
- “Automated analysis of tumor microenvironment in triple negative breast cancer without complete pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Predictive factor of relapse” financed by Institute of Health Carlos III in Spain, headed by dr Merylene Lejeune from Molecular Biology and Research Section, Hospital Verge de la Cinta w Tortozie, developed from 1.01.2014 to 31.12.2016,
- „Web-based platform for the computer analysis of microscopic images to support the pathological diagnosis” financed by The National Center for Research and development (NCPBiR), headed by DSc Tomasz Markiewicz, prof. from Warsaw University of Technology, developed from 27.09.2013 to 30.10.2016.
The project titled „Supporting software to assist pathologist in evaluation of immunohistochemically stained tissue samples of breast cancer stained with DAB&H” financed by National Sciences Center (NCN), headed by Łukasz Roszkowiak is has been in development since 11.09.2014.
Equipment
In the Laboratory, there is an optical microscope, working in bright field or fluorescence modes. It has capabilities of digitally recording sequences with PC-controlled irises (for UV and visible light) and microscope table in Z axis.
Keywords: image analysis, image segmentation, microscopic images, time laps microscopy, cell behaviour, cell movement, analysis of WSI, correction and standardization of scanned images of stained tissues, digital pathology, computer-aided quantitative morphometry




















